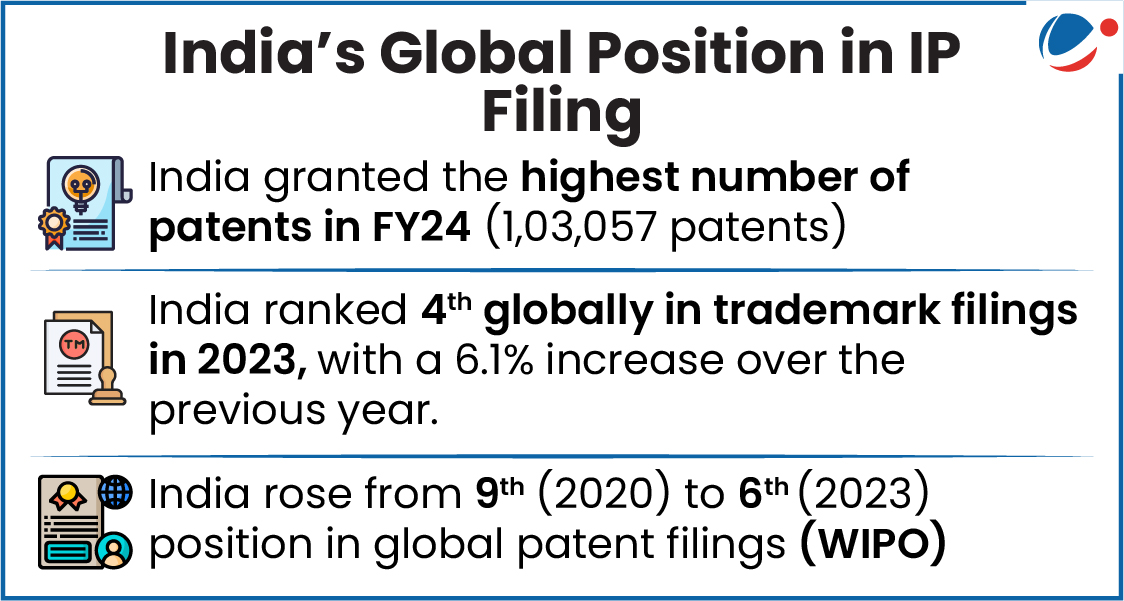
Why in the news?
India's Intellectual Property (IP) filings rose by 44% in last 5 years, led by a 380% surge in Geographical Indications.
Reasons for Increase in IP Boom
- Legal & Procedural Simplification of IP laws & rules E.g. Patent examination timeline reduced from 48 months to 31 months and mandatory e-submission for patent documents.
- Modernization of IP Offices: IP offices have been digitized with a comprehensive e-filing system, leading to over 95% of applications being filed online.
- International standards: E.g. adoption of international classification under Locarno Agreement for Industrial Designs.
- Locarno agreement is an international agreement under the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) signed in 1968.
- Awareness & Capacity Building E.g. SPRIHA Scheme aims to integrate IPR education into higher learning institutions across the country
- National Intellectual Property (IP) Awards: To recognize and reward the top achievers for their IP creations and commercialization.
- Other: Fee Concessions (10% fee reduction for online filings), Digital initiatives (IP Sarthi Chatbot for applicant support and IP Dashboard to provide real-time IP data) and use of AI and Machine Learning etc.
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- Definition: IPR are the rights given to persons over the creations of their minds. They usually give the creator an exclusive right over the use of his/her creation for a certain period of time.
- 8 types of IPR are covered under IPR Policy Management (IPRPM) framework: (i) Patents, (ii) Trade mark, (iii) Industrial Designs, (iv)Copyrights, (v) Geographical Indications, (vi) Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Layout Design, (vii) Trade Secret, and (viii) Plant Varieties.
- Administered by: Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks which is under the control of the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Act on Layout-Design of Integrated Circuits is administered by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Ministry of Agriculture administers the Act on Plant Variety.
Details of legal and regulatory considerations for different IP areas:
IPR Area | Subject | Legal Provision | Term of Protection |
Geographical Indication (GI) | Goods bearing unique characteristics due to geographical linkage - agricultural goods, natural goods, manufactured goods, handicrafts and foodstuff. | Geographical Indications Act 1999 & GI Rules 2002 amended in 2020. | 10 years, Renewed for 10 years on payment of additional fees |
Design | New or original designs (Ornamental / visual appearance discernible to the human eye) which can be replicated industrially. | The Design Act, 2000 & Designs (Amendment) Rules 2021 | 10 + 5 years |
Patents | Must qualify requirements of being novel, Inventive and having industrial utility. | The Patents Act, 1970 & Patent Rules, 2003 (Amended in 2014, 2016, 2017, 2019, 2020 and 2021) | 20 years |
Copyright | Creative, artistic, literary, Musical and audio-visual works | The Copyrights Act, 1957 &Copyrights Rules 2013 amended in 2021. | Author- Lifetime+ 60 years; Producers - 60 years Performers- 50 years; |
Trademarks | Protects brand name, logo, and design for a business or commercial enterprise. | The Trade Marks Act, 1999 & Trademark Rules 2017 | 10 years; renewed for 10 years on payment of additional fees |
Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Designs (SICLD) | A layout of transistors and other circuitry elements including lead wires connecting such elements and expressed in any manner in semiconductor integrated circuits. | The Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout- Design Act, 2000 & Rules, 2001. | 10 years |
Trade Secret | Confidential information having commercial value. | Common Law approach (covered through Contract Act, IP Act, and Copyright etc.) | Till the time confidentiality is safeguarded. |
Plant Varieties | Traditional varieties and landraces, all developed varieties (non-traditional and non-landrace) in trade/use for older than 1 year and not older than 15 years or 18 years (in case of trees and vines), and new plant varieties. | Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers Rights Act (PPVFRA), 2001 | 6-10 years. |
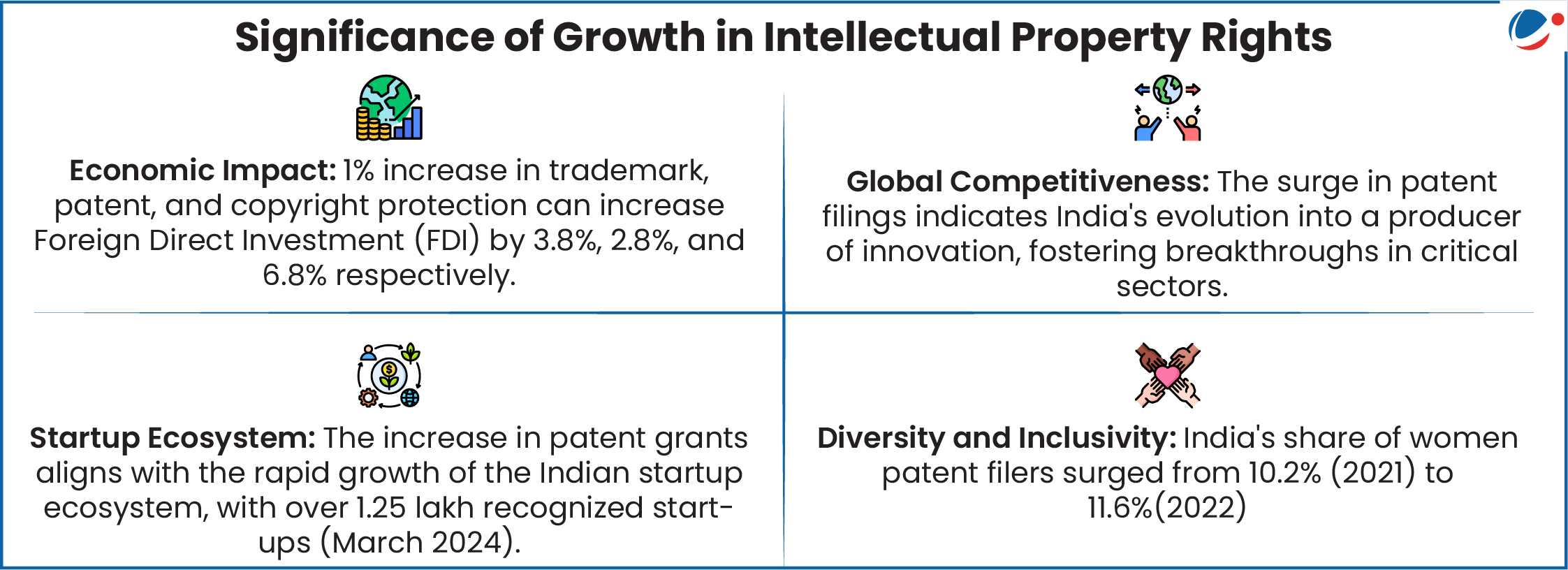
Challenges related to IPR in India:
- Low Research and Development (R&D) Spending: India spends a mere 0.7% of its GDP on R&D, significantly lower than countries like China (2.1%) and Brazil (1.3%).
- Patent Disputes and Evergreening: The pharmaceutical sector often faces issues related to patent evergreening, where companies make minor modifications to existing drugs to extend their patent life.
- Section 3(d) of the Patents Act, 1970, prevents this, leading to disputes with multinational corporations.
- Compulsory Licensing Concerns: In the pharmaceutical sector, the government can allow the production of patented products (e.g., medicines) without the patent holder's consent.
- While this ensures access to essential medicines, it has led to tensions with global pharmaceutical companies.
- IP Financing in Nascent Stage: Due to lack of awareness, complexities in IP valuation, reliance on traditional tangible assets, and vulnerability of IP as collateral.
- IP financing is the use of IP assets (trade marks, design rights, patents and copyright) to gain access to credit.
- Ambiguity of "Patent Pending" Status: Unlike countries like the USA, India lacks a clear provision for marking products as "patent pending," which could deter competitors and act as a marketing tool.
- Other: Delays in IPR Granting and Backlog, Weak Enforcement of IPR Laws, Commercialization Gap (High filings don't guarantee successful market-ready products) etc.
Way Forward
- Holistic Review of National IPR Policy: To address new and emerging trends in innovation, identify implementation gaps, and incorporate changes for expanding innovation ecosystem and IP financing.
- Strengthen State Government Participation: To formulate and implement their own IPR policies, focusing on awareness, innovation in educational institutions, establishing State-level Innovation Councils, and curbing IP crimes.
- Strengthening Enforcement Mechanisms: Improve coordination between law enforcement, customs, and IP offices and provide specialized IPR training. Establish more specialized IPR courts with technically trained judges.
- Create IP Fund: Establish a dedicated IP fund to support initiatives fostering IP culture in remote and traditional knowledge-rich regions, such as tribal belts, hilly, and North-East states.
- Enhancing International Collaboration e.g. Cooperate with global IP bodies (e.g., WIPO) and adopt best practices.
- Ensuring that trade agreement's IP provisions balance innovation, public health, and national interest.
- Other: Promoting Innovation & Research through R&D incentives (tax breaks, grants), Strengthening Cyber security & Digital IPR Protection to combat online piracy, enhance IP awareness through educational initiatives etc.







