Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released 2024 list of Domestic Systemically Important Banks (D-SIBs)
- State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank continue to be identified as D-SIBs in the RBI’s 2024 list.
About D-SIBs
- D-SIBs are systemically important due to their size, cross-jurisdictional activities, complexity and lack of substitute and interconnection.
- It also means that the bank is too big to fail.
- If DSBs fail, there would be significant disruption to the essential services of the banking system and the overall economy.
Declaration of D-SIBs
- Based on the D-SIBs Framework of RBI (2014).
- Framework is based on Basel Committee on Banking Supervision’s (BCBS’s) framework.
- Banks having size as a percentage of GDP equal to or more than 2% are considered for D-SIB list.
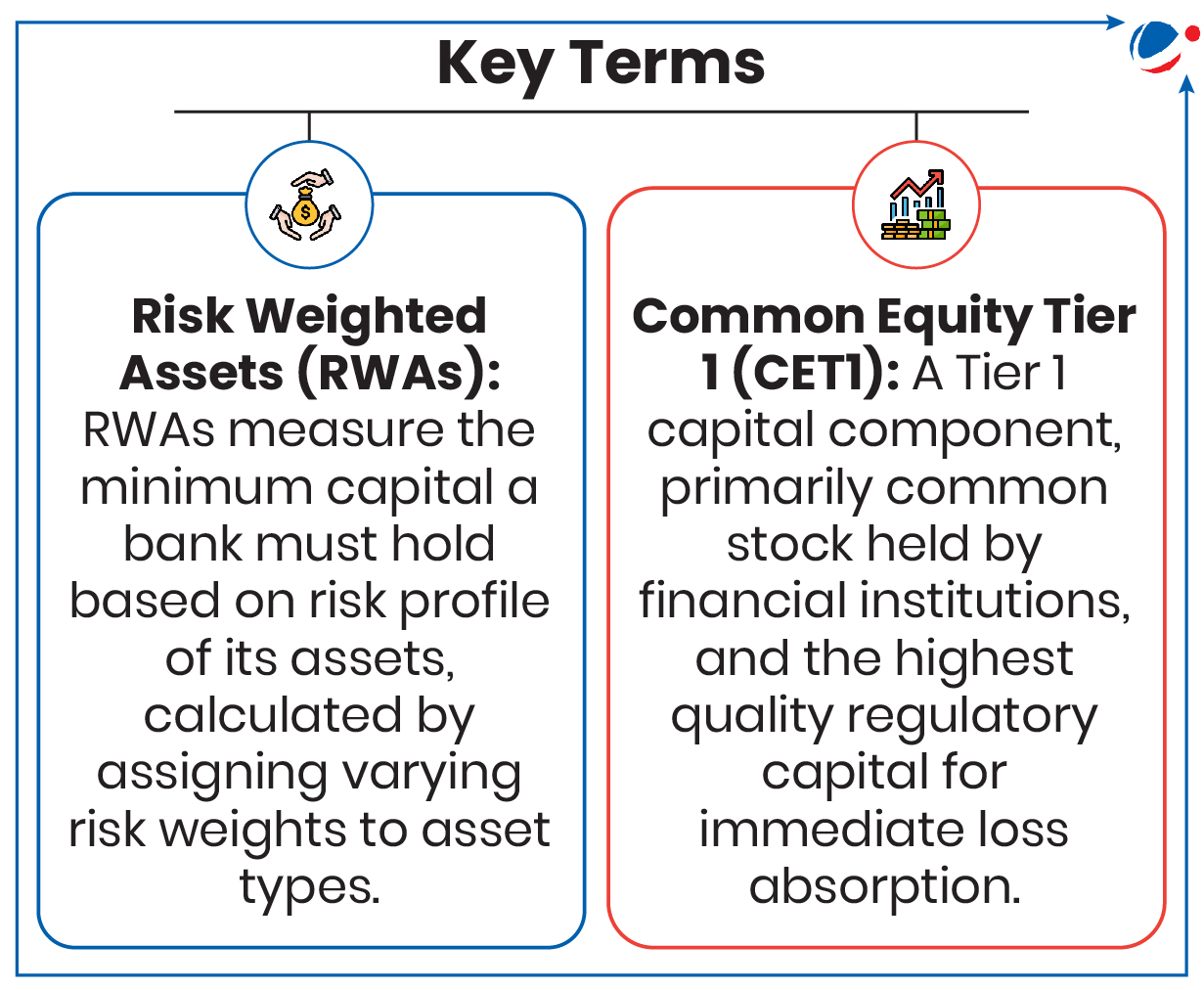
- Banks are placed in 5 buckets on the basis of Additional Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) requirement as a percentage of Risk Weighted Assets (RWAs).
- Bucket 1 banks have to maintain lowest CET1 and Bucket 5 banks have to maintain highest.
- In case a foreign bank having branch presence in India is a Global Systemically Important Bank (G-SIB), it has to maintain additional CET1 capital surcharge.
- Financial Stability Board (FSB) releases the list of G-SIBs.
- Tags :
- Domestic Systemically Important Banks
- D-SIBs
‘The State of Food and Agriculture 2024’ report released by FAO
Report emphasizes on value-driven transformation of agrifood systems and builds on the estimates of the previous edition on global hidden costs of agrifood systems (journey of food from farm to table).
- Hidden cost refers to external costs (i.e., negative externalities) or economic losses triggered by other market or policy failures.
Key findings of the report

- Hidden Costs: Industrial and diversifying agrifood systems contribute maximum to global quantified hidden costs (around 5.9 trillion 2020 PPP dollars), dominated by health hidden costs linked to non-communicable diseases.
- Unhealthy dietary patterns (like low intake of whole grains, high intake of sodium, etc.) account for 70% of all quantified hidden costs.
- Other contributing factors include: Social costs (due to undernourishment and poverty); environmental costs (emission of greenhouse gases, etc.).
- India-related findings: India’s total hidden costs stands around $1.3 trillion annually (3rd largest after China and the USA), largely driven by unhealthy dietary patterns.
Major Recommendations on transforming the Agrifood value chains
- In industrial agrifood systems (Long value-chains with high urbanization): Upgrade food-based dietary guidelines to an agrifood systems approach, mandatory nutrient labels and certifications, and information campaigns, etc.
- In traditional agrifood systems (Short value-chains with low urbanization): Complement conventional productivity-enhancing interventions with environmental and dietary levers to avoid the increase in environmental footprint.
- Tags :
- ‘The State of Food and Agriculture 2024’ report
World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
Indian Council of Agricultural Research-National Research Centre on Equines (ICAR-NRC Equine) in Haryana has been granted WOAH Reference Laboratory status.
- This recognition is specifically for its expertise in Equine Piroplasmosis disease.
- Equine Piroplasmosisis caused by tick-borne protozoan parasites, affects horses, donkeys, mules, and zebras.
About WOAH
- An intergovernmental organization founded in 1924.
- Objective: Disseminating information on animal diseases and improving animal health globally.
- Members: 183 including India.
- HQ: Paris, France
- Tags :
- World Organisation for Animal Health
Articles Sources
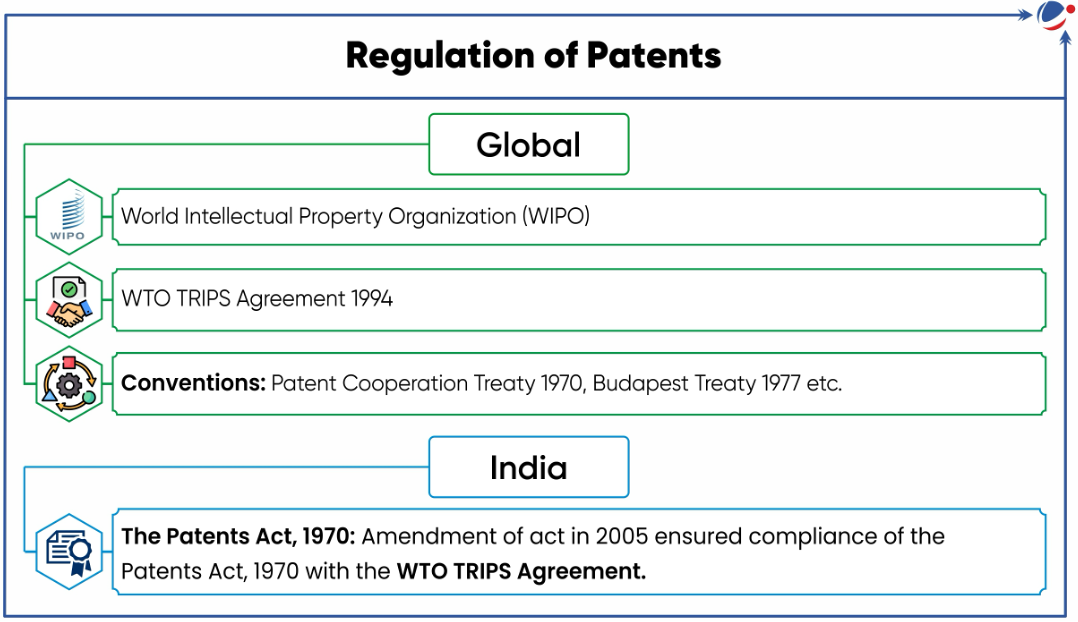
World Intellectual Property Indicators 2024 report
World Intellectual Property Indicators 2024 report released by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).
- According to report, India experienced significant growth in intellectual property filings, with patents filings doubling between 2018 and 2023.
Other Key Findings related to India:
- Patents: India is ranked 6th globally with 64,500 Patent Filings and country’s Patent-to-GDP ratio surged to 381 from 144 (2013 to 2023).
- Trademarks: India’s IP office hold the second highest of active registrations globally and now India ranks 4th globally in trademark filings.
- Industrial Design Filing: Ranked 10th globally with a 36% increase in 2023, showing significant growth in creative design.
Factors behind Surge in Patent filing:
- Government Initiatives and Policy Support: E. g. Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2024 (reduced renewal fee and filing frequency time) simplified patent process, National IPR Policy, 2016 etc.
- Timely clearance of applications: India granted 1.03 lakh patents in financial year 2023-24.
- Strengthened IP Infrastructure: Digitization of patent filing processes, establishment of IPR facilitation centers etc.
Challenges/Issues related to Patents in India:
- Abolition of Intellectual Property Appellate Board: Leading to creation of a void in handling appeals in IP cases.
- Evergreening of Patents: To extend patent period, guaranteeing monopoly over drugs.
- Other Issues: Compulsory licensing, lack of fixed timelines for each step in procedure etc.
- Tags :
- World Intellectual Property Indicators 2024 report



