Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet approved the Export Promotion Mission (EPM).

More on the News
- This Mission was announced in the Union Budget 2025–26.
- Also, the Cabinet approved the introduction of the Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters (CGSE).
About Export Promotion Mission (EPM)
- Vision: Provides a comprehensive, flexible, and digitally driven framework for export promotion.
- Financial Outlay: Rs. 25,060 crores
- Timeline: Six years (FY 2025–26 to FY 2030–31)
- Targeted Sectors: Priority support will be extended to sectors impacted by recent global tariff escalations, such as textiles, leather, gems & jewellery, engineering goods, and marine products.
- Mission Architecture: It will operate through two distinct but integrated sub-schemes:
- Niryat Protsahan (Financial Support):
- Designed to improve access to affordable trade finance for diversification into new markets.
- Niryat Disha (Non-Financial Support):
- Designed to enhance the market readiness and competitiveness of exporters.
- Ways under it includes Export quality and compliance support, assistance for international branding, export warehousing and logistics, etc.
- Niryat Protsahan (Financial Support):
- Implementing Agency: Directorate General of Foreign Trade
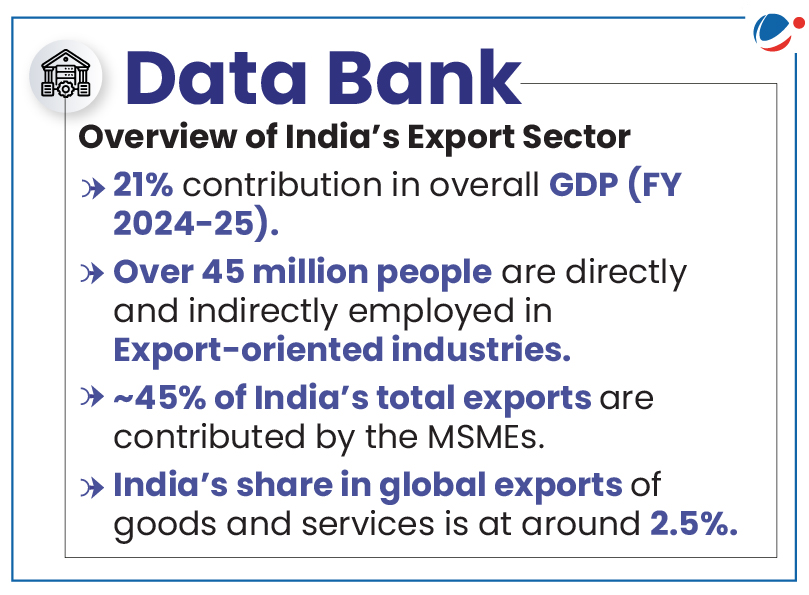
Need of Export Promotion Mission (EPM)
- Consolidation of Existing Schemes: It integrates and modernizes key existing schemes e.g. Interest Equalisation Scheme and Market Access Initiative.
- Logistics Challenges: Inadequate Infrastructure and Transit Delays, Sharp Rise in Freight Costs & Shipping Disruptions (E.g., disturbances in the Red Sea route), etc.
- Market Access Challenges: Limited Visibility and Buyer Connections, Identifying new markets, etc.
- Regulatory Challenges: This includes regular documents such as a certificate of origin, quality inspection certificate, and packing list, among others.
- International constraints
- Competition: E.g. Indian products are less competitive in comparison with Chinese products due to high production costs, low innovation, etc.
- Trade barriers and tariffs (increasing global protectionist tendencies): E.g., recently, the U.S. imposed a steep 50% tariff on Indian goods, significantly reducing India's exports to the U.S., which is India's largest export destination.
- Other constraints: Issue of quality standards, Supply chain disruption, etc.
Other Key Government Initiatives to Strengthen India's Export Landscape
|
What more can be done to Promote Exports?
- Finalising Free Trade Agreements (FTA): Several upcoming free trade agreements can also be negotiated better to improve market access (e.g. Europe, central Asia etc.) and favourable trading terms.
- Harness demand for high-value technical services: For instance, specialised technical expertise in the fields of R&D, manufacturing services, supply chain management and maintenance and repair.
- Strengthening MSME exports: Through increased MSME participation in trade shows and exhibitions. MSMEs should also be trained on important aspects of export procedures, documentation, and standards.
- Strengthen Innovation & Value Addition: E.g., Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) launched BHARATI (Bharat's Hub for Agritech, Resilience, Advancement and Incubation for Export Enablement) to promote innovation and create new export opportunities for young entrepreneurs.
- Unlock E-Commerce Exports: E.g., create separate customs supervision codes for e-commerce exports.
- Create National Trade Network (NTN): Proposed unified digital platform to centralize all export-import processes (customs, DGFT, banks, ports) into one system.
- Implementing NTN would prove beneficial in minimizing transaction costs and addressing the informational asymmetry.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Exporters (CGSE)
|
Conclusion
EPM provides a unified and digitally driven framework to overcome fragmented export schemes and strengthen India's global competitiveness. By addressing key challenges like logistics gaps, quality standards, and market access, it aims to drive sustained and diversified export growth.







