Why in the News?
India launched its 1st indigenous CRISPR-based gene editing therapy called BIRSA-101 for Sickle Cell Disease.

More on News
- It has been developed by CSIR–Institute of Genomics & Integrative Biology (IGIB).
- It has been called BIRSA-101 as it has been dedicated to Bhagwan Birsa Munda on his 150th birth anniversary.
- A technology transfer agreement has been signed between CSIR-IGIB and Serum Institute of India which aims to enable scalable, affordable enFnCas9 CRISPR-based therapies for Sickle Cell Disease and other genetic disorders.
CRISPR Technology and Mechanism
- CRISPR stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
- It is a gene-editing technology to selectively modify the DNA of living organisms.
How does it work?
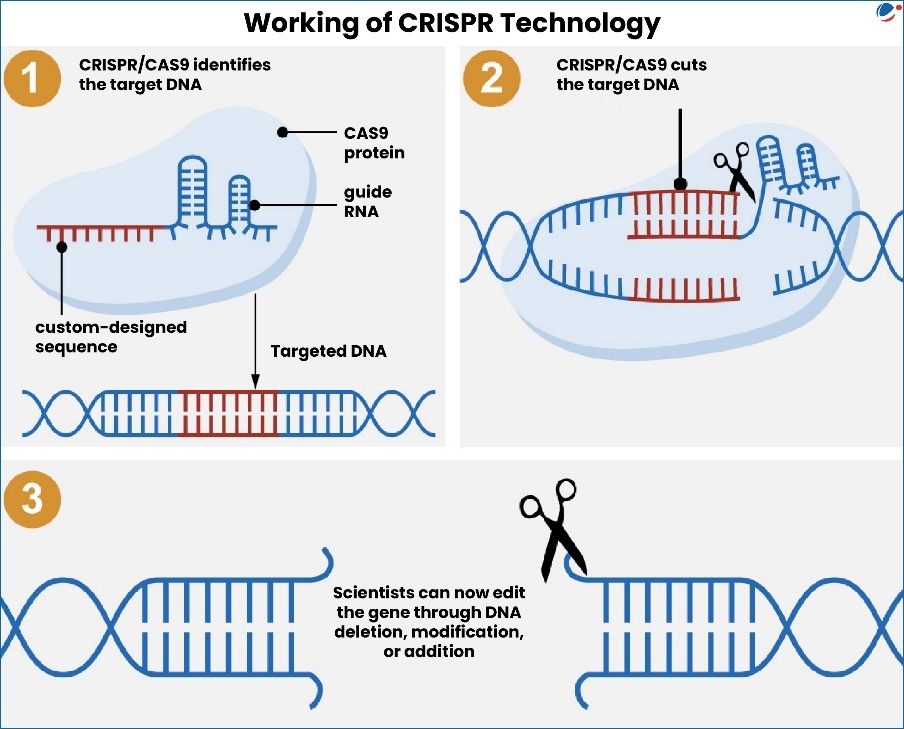
- CRISPR leverages a natural defense mechanism of bacteria to cut DNA at a specific location.
- When bacteria are attacked by a virus, they record a section of the virus's DNA in their own DNA.
- Storing part of the virus's genetic code allows the bacteria to "remember" it.
- When the same type of virus attacks again, the bacteria use a specific CRISPR-associated protein number 9 (CAS9) to cut the virus's DNA, destroying the virus.
- In the laboratory, scientists use this same CRISPR/CAS9 system to identify and cut a specific DNA sequence.
- Main Components:
- Cas9 Protein: The system uses a Cas protein called Cas9, which acts like molecular scissors to cut DNA.
- Guide RNA: A guide RNA tells Cas9 where to cut, and the DNA is cut exactly at the spot chosen by this guide.
- Genome Editing Tools
- CRISPR-Cas9: It uses a small piece of RNA to guide the Cas9 "cutting" protein to the exact spot in the DNA.
- Homing Endonucleases (Meganucleases): These are natural enzymes that can find and cut long sections of DNA.
- Zinc-Finger Nucleases (ZFNs): They use special protein parts to find the right place in the DNA and then cut it.
- TALE Nucleases (TALENs): These tools use two parts that come together to cut DNA at a chosen spot.
Related NewsTnpB-Based TechnologyIndian scientists at ICAR–CRRI (Central Rice Research Institute) Cuttack have developed a new genome-editing tool for plants using TnpB proteins which has been granted patent.
GlowCas9
|



