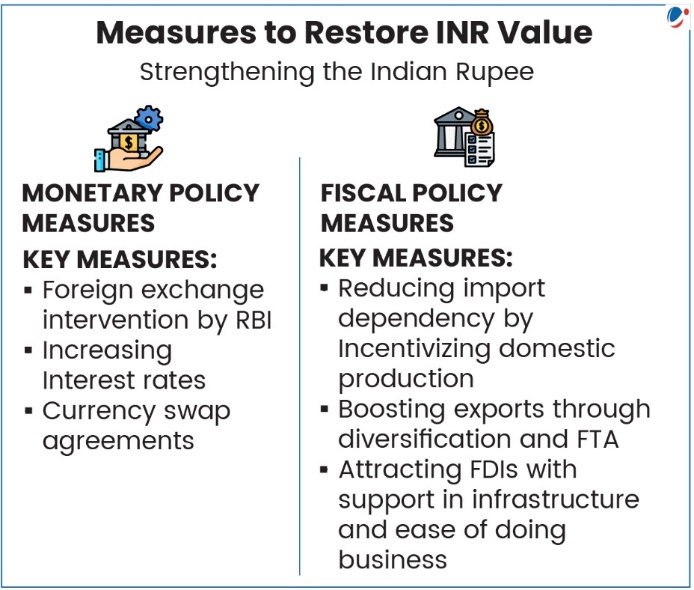
Indian Rupee (INR) breached 90-mark against US Dollar.
Despite strong domestic macroeconomic indicators (8.2% GDP growth, near 1% inflation, lower crude prices, etc.), INR depreciated by more than 5% in 2025.
- Depreciation of the rupee occurs when its value declines relative to foreign currencies in the open market.
Primary Factors Driving Depreciation
- Uncertainty over US-India Trade Deal: the imposition of steep US tariffs (up to 50%) on Indian goods challenges export competitiveness and dents investor confidence.
- Capital Outflows: Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) have pulled significant funds, often treating India as a liquidity source to pursue opportunities elsewhere.
- Widening Trade Deficit: driven by high demand for gold, electronics, and machinery, while exports to major markets, including the US, have softened.
- Speculative Investment: continuous dollar demand from importers who are front-loading their dollar purchases on expectations of further rupee weakening.
Key Impacts on Indian Economy
- Negative Impact:
- Imported Inflation: as India imports a large proportion of its crude oil (90%), edible oils, etc.
- Increased Subsidy Burden: Higher import prices for fertilizers will swell the government’s subsidy bill.
- Higher Cost of Overseas Liabilities: Companies with dollar-denominated debt face higher repayment and interest servicing costs.
- Positive Impact:
- Export Competitiveness: makes Indian exports cheaper and more competitive in the global market.
- Remittances: A weaker rupee could make remittances from overseas more attractive.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Government of India has undertaken the Global Indices for Reforms and Growth (GIRG) initiative for driving reforms and growth in the country.
About Global Indices for Reforms and Growth (GIRG) Framework
- Purpose: It monitors India’s performance on selected global indices to identify gaps and guide evidence-based reforms.
- Coverage: Tracks 26 indices across four broad themes: economy, governance, development, and industry, released by 16 international agencies.
- Implementation: 17 nodal ministries are assigned specific indices.
- The Development Monitoring and Evaluation Office (DMEO), NITI Aayogcoordinates data quality checks, methodology review, and reform implementation.
- Significance: Enhances transparency, strengthens policymaking, boosts India’s global competitiveness, and supports cooperative and competitive federalism.
Article Sources
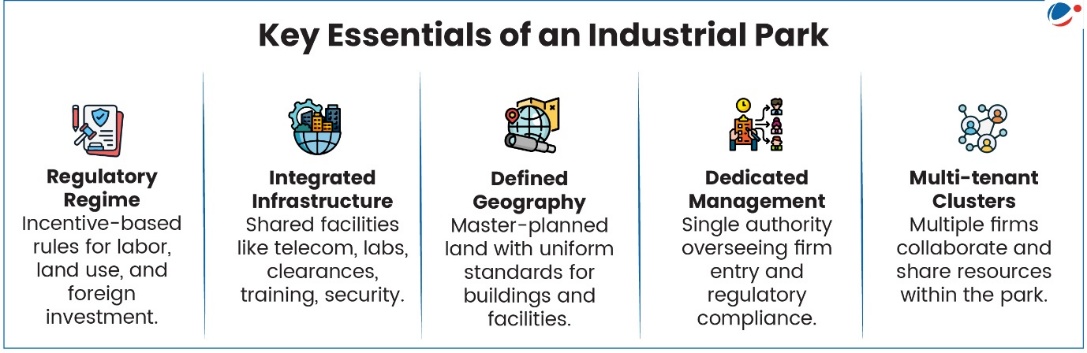
1 sourceIndustrial Parks are emerging as a key pillar of India’s Innovation and Industrial Growth. Developed in partnership with state governments and private sector, they offer shared infrastructure, streamlined approvals and a predictable regulatory environment.
Status of IP in India
- Currently, India has more than 4,500 industrial parks as per India Industrial Land Bank (IILB).
- 306 plug-and-play industrial parks and 20 parks and smart cities are being developed under National Industrial Corridor Development Corporation (NICDC).
Key Benefits offered by Industrial Parks
- Economic Growth: Integrate scarce factors of production, generate higher productivity and operational efficiency, attract FDI (India among the top 5 global destinations for greenfield projects as per UNCTAD), creating jobs, and improved wages, etc.
- Environmental and Social Responsibility: Promote eco-friendly practices, support resource efficiency, etc., along with offering gender sensitive facilities, health and security systems to employees.
Initiatives taken to promote them
- Plug-And-Play Industrial Parks: Union Budget 2025-26 allocated Rs. 2,500 crores for their development.
- India Industrial Land Bank (IILB): Developed by Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) as a centralized Geographic Information System (GIS)-enabled platform offering spatial and non-spatial information on industrial land.
- Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS): Comprehensive framework for assessing performance and quality.
- IPRS 3.0 was launched in September 2025 with enhanced parameters on sustainability, skill linkages, digitalization, etc.
- Ease of Doing Business Reforms: Through National Business Reforms Action Plan (BRAP), 2014; Goods and Services Tax (GST), reducing compliance burden, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceSEBI reclassified REITs as equity instruments to boost participation by mutual funds and SIFs, while retaining Infrastructure investment trusts (InvITs) under hybrid category.
- Equity instruments, also known as shares, and capital shares in particular, give holders property rights to the company.
- A hybrid security blends the features of two financial instruments into one asset, usually combining aspects of debt and equity.
About Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
- Definition: It is a company that owns, operates, or finances income-generating real estate and sells shares to raise capital to do so.
- REITs are an alternative investment option for people who cannot afford to invest directly in real estate.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Central Board of the RBI approved the risk-based deposit insurance premium framework.
- It will replace the current flat-rate system (of 12 paise per Rs 100 deposit).
- The main objective of deposit insurance is to protect depositors’ money against bank failure.
What is a risk-based deposit insurance premium framework?
- In it, the insurance premium charged to banks depends upon their risk profile.
- Safer, well-managed banks pay lower premiums; riskier banks pay higher premiums.
- Objective
- To incentivise sound risk management and reward prudent behavior with lower costs.
- Reduce moral hazard by discouraging banks from taking excessive risks.

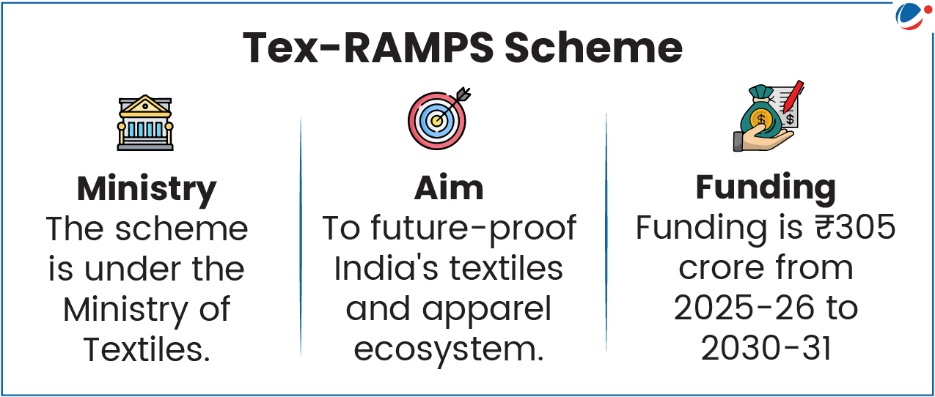
Government has approved the Textiles Focused Research, Assessment, Monitoring, Planning and Start-up (Tex-RAMPS) Scheme.
Key Components of ‘Tex-RAMPS’ Scheme
- Research & Innovation: in smart textiles, sustainability etc.
- Data, Analytics & Diagnostics: including employment assessments, supply chain mapping, etc.
- Real-time Integrated Textiles Statistical System (ITSS): to support structured monitoring and strategic decision-making.
- Capacity Development & Knowledge Ecosystem: Strengthening of State-level planning, dissemination of best practices.
- Start-up & Innovation Support: Support for incubators, hackathons, and academia-industry collaborations.
Article Sources
1 sourceParliament has passed the Health Security se National Security Cess Act 2025 to mobilise additional fiscal resources for strengthening defence preparedness, public-health systems, and national security.
Key Features of The Act
- Introduced to create a clear legal framework for a special excise cess.
- Introduces a capacity-based excise cess on machinery/processes used to manufacture specified goods, initially pan masala.
- Cess proceeds will support national security and public health via the Consolidated Fund of India.
Article Sources
1 sourceReleased by Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying recently.
Key Production Estimates
Sector | Key Highlights |
Milk |
|
Egg |
|
Meat |
|
Wool |
|







