Why in the News?
According to Annual report for 2024 published by World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) found that India has the highest number of dope cheats in the world for the third year.
Meaning and Status in India
- Doping is defined as the consumption of prohibited substances (Performance Enhancing Drugs) or methods to unfairly improve sporting performance and to gain an advantage over competitors.
- India reported 260 positive cases for prohibited performance-enhancing drugs with a positivity rate of 3.6%.
- India is followed by France and Italy in absolute number of doping offenders.

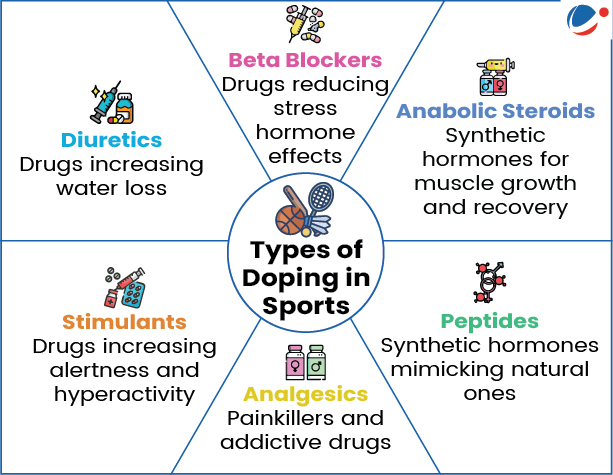
Causes of Doping
- Attractive incentives and assured rewards: E.g. Medal winners at national games receive out-of-turn government jobs, cash awards.
- Easy access to prohibited substances: E.g. Over-the-counter availability of anabolic steroids in local gyms and pharmacies without prescription.
- Inadequate education and awareness: E.g. Consuming supplements or medicines prescribed by local trainers without WADA compliance knowledge.
- Deficient sports infrastructure and institutional support: Poor training facilities, limited exposure, and inadequate scientific support compel athletes to resort to shortcuts like doping.
- Societal and familial pressure: Sports is often not viewed as a viable career in India, leading to intense pressure from coaches, families, and society on athletes to deliver quick success.
- Weak testing and monitoring mechanisms: Anti-doping oversight is largely absent in smaller tournaments and district competitions, reducing deterrence and increasing the likelihood of violations.
- Weak Governance Structure: Nepotism, financial irregularities, unfair selections, and lack of transparency, leading to athlete mistreatment and doping scandals.
- Withdrawal of Funding to WADA: Dependent upon developed countries affects the movement for doping-free sport. E.g. USA decision to withhold funding to WADA in 2025.
Initiatives taken to stop Doping in India
|
Conclusion
Achieving a "Dope Free India" requires a transformative shift from reactive enforcement to a holistic ecosystem of prevention and integrity. By integrating advanced scientific monitoring like the Athlete Biological Passport with robust education for athletes and their support networks, the strategy ensures that compliance is driven by awareness.




