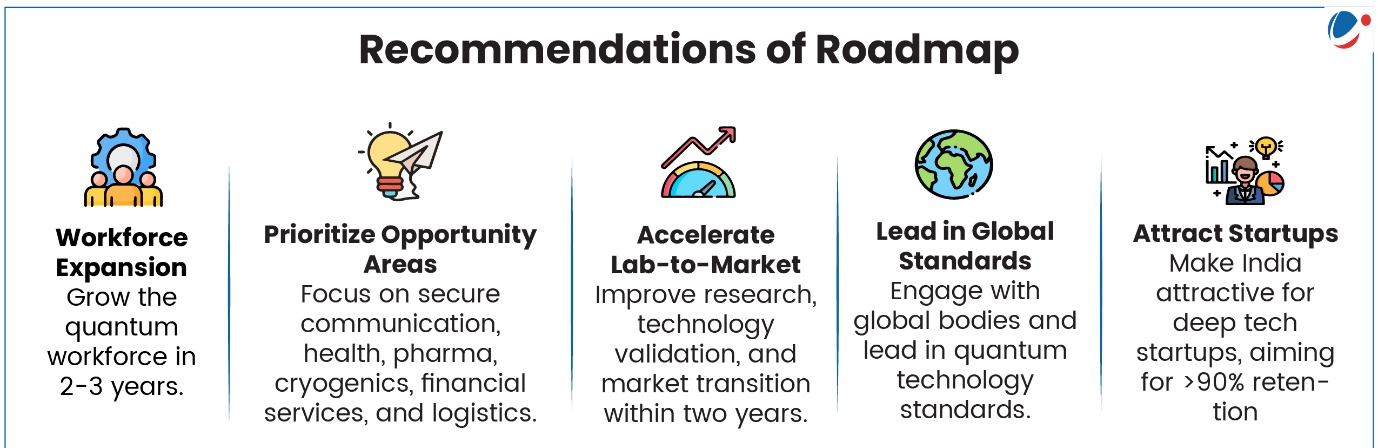
NITI Aayog & IBM unveiled roadmap to make India a top3 Quantum Economy by 2047.
- The roadmap “Transforming India into a leading Quantum-Powered Economy” will help to build a home grown quantum computing ecosystem and capture a major share of the global quantum market.
- It aims to incubate at least 10 globally competitive quantum startups, each surpassing USD 100 million in revenue and capturing over 50% of the value in the global quantum software and services market by 2035.
Status in India of Quantum Technology
- Talent Pool: India ranks 2nd globally in the number of graduates in quantum-relevant fields (approximately 91,000), behind only the EU.
- State-Level Competition: Different states are actively building their own ecosystems. For example, Karnataka has established the Quantum Research Park (QuRP), and Andhra Pradesh recently launched the Amaravati Quantum Valley (AQV).
About Quantum Technology
|
Article Sources
1 sourceISRO’s LVM3-M6 Mission successfully placed the Bluebird Block-2 Satellite in Low Earth Orbit (LEO).

- LVM3-M6 is the Sixth Operational Flight of LVM3 and the third dedicated commercial mission to launch the BlueBird Block-2 satellite of AST SpaceMobile, USA.
- Launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, the mission is a part of commercial agreement between NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) and AST, a US based Company.
- Incorporated in 2019, as a wholly owned Government Company under Department of Space, NSIL serves as the commercial arm of ISRO.
About Blue Bird Block -2
- Part of a global LEO constellation: Provides direct-to-mobile connectivity through satellite; Enable 4G and 5G voice and video calls, texts, streaming, and data, etc.
- LEO is an orbit relatively close to Earth’s surface with an altitude around 160-2000km, useful for satellite imaging and is the site of International Space Station (ISS).
- Key Features: 223m² phased array, making it largest commercial communications satellite ever deployed into LEO.
- It is also the heaviest payload (6,100 kg) to be launched by LVM3.
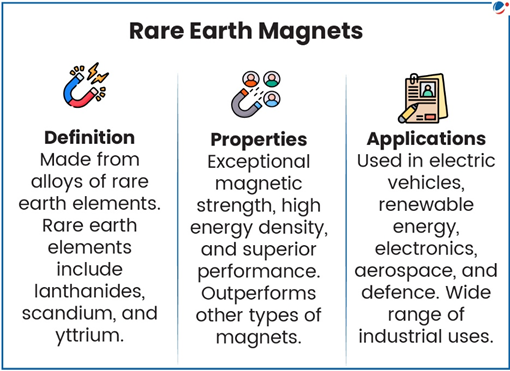
The Union Cabinet has approved the “Scheme to Promote Manufacturing of Sintered Rare Earth Permanent Magnets (REPMs)” to secure India’s long-term supply of rare earth magnets and reduce dependence on imports.
- Sintering is a process where magnet materials are heated to high temperatures without melting. It strengthens the magnets, enhances magnetic performance, and makes them more resistant to corrosion.
Key Features of Scheme:
- Financial Outlay: ₹7,280 crore.
- Incentive Structure:-
- ₹6,450 crore as sales-linked incentives over five years.
- ₹750 crore as capital subsidy for facility setup.
- Incentive Structure:-
- Objective: Establish 6,000 Metric Tons per Annum (MTPA) of integrated REPMs manufacturing in India.
- Beneficiaries Allocation:
- The 6,000 MTPA capacity will be allocated to five beneficiaries through global competitive bidding.
- Each beneficiary may receive up to 1,200 MTPA capacity.
- End-to-End Manufacturing Integration: It supports the creation of facilities that cover the complete processing facilities:-
- Rare earth oxides → metals→ alloys→ finished rare earth permanent magnets
- Total Duration of the Scheme: 7 years
- 2 years: facility setup (gestation period)
- 5 years: incentive disbursement on sales
Article Sources
1 sourceGoogle CEO has announced that the company has begun work on a long-term research initiative, Project Suncatcher aiming to put solar powered data centers in space.
About Project Suncatcher
- It is a Google initiative aimed at building solar-powered satellite constellations capable of performing large-scale machine learning computations in space.
- Satellites will be equipped with Google’s Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) .
- Advantages:
- Avoids environmental impact of Earth-based data centres.
- Reduces vulnerability to power outages, undersea cable cuts, and natural disasters.
- Facilitates data sovereignty, as outer space is not subject to national jurisdiction under the Outer Space Treaty of 1967.
India launches DHRUV64 microprocessor.
About DHRUV64
- It is first 1.0 GHz, 64-bit dual-core first fully indigenous microprocessor.
- Microprocessors are the brains of modern electronic devices such as mobiles, computers, etc.
- Developed by: The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) under the Microprocessor Development Programme (MDP).
- Other microprocessors developed by India: SHAKTI (2018, IIT Madras), AJIT (2018, IIT Bombay), VIKRAM (2025, ISRO–SCL), and THEJAS64 (2025, C-DAC).
- The next-generation Dhanush and Dhanush+ processors are under development.
- Significance: India consumes around 20% of all the microprocessors manufactured globally

This is the first-everpolitical declaration to jointly address Noncommunicable Diseases (NCDs) and mental health, adopted at the 80th United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), with specific targets for 2030 (refer infographic).
About the Declaration
- Expanded Scope: New NCDs areas included like oral health, lung health, childhood cancer, etc.
- New Determinants Covered: Air pollution, clean cooking, lead exposure & hazardous chemicals.
- Digital Health Risks: included for the first time, like harm from social media, excessive screen time, misinformation & disinformation.
- Stronger regulation: For tobacco, unhealthy foods, trans fats & e-cigarettes.
- Whole-of-government & whole-of-society approach: includes engagement of civil society, youth, persons with disabilities, private sector.
- Clear accountability: With the UN Secretary-General reporting on targets & WHO support.
Significance of the declaration
- NCDs cause ~18 million premature deaths/year.
- They tend to be of long duration and are the result of a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental and behavioural factors.
- Mental health conditions affect 1+ billion people globally.
- They both are driven by common, preventable risk factors: tobacco, unhealthy diets, alcohol, inactivity, air pollution.
Initiatives taken in India for
|
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) directed its regional offices to collect samples of eggs for testing the presence of nitrofurans residues.
About Nitrofurans
- Nitrofurans are a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics. E.g. furazolidone, nitrofurazone.
- They commonly used as veterinary drugs for antibacterial and anti-inflammatory purposes.
- However, they are banned for use in food-producing animals in India.
- Concerns: Genotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic, residues may persist even after cooking.



