Why in the News?
The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) recently tabled a performance audit report in Parliament titled "Skill Development under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana".
More on the News
- The report flags serious data integrity lapses, infrastructure gaps, and low placement rates in the scheme.
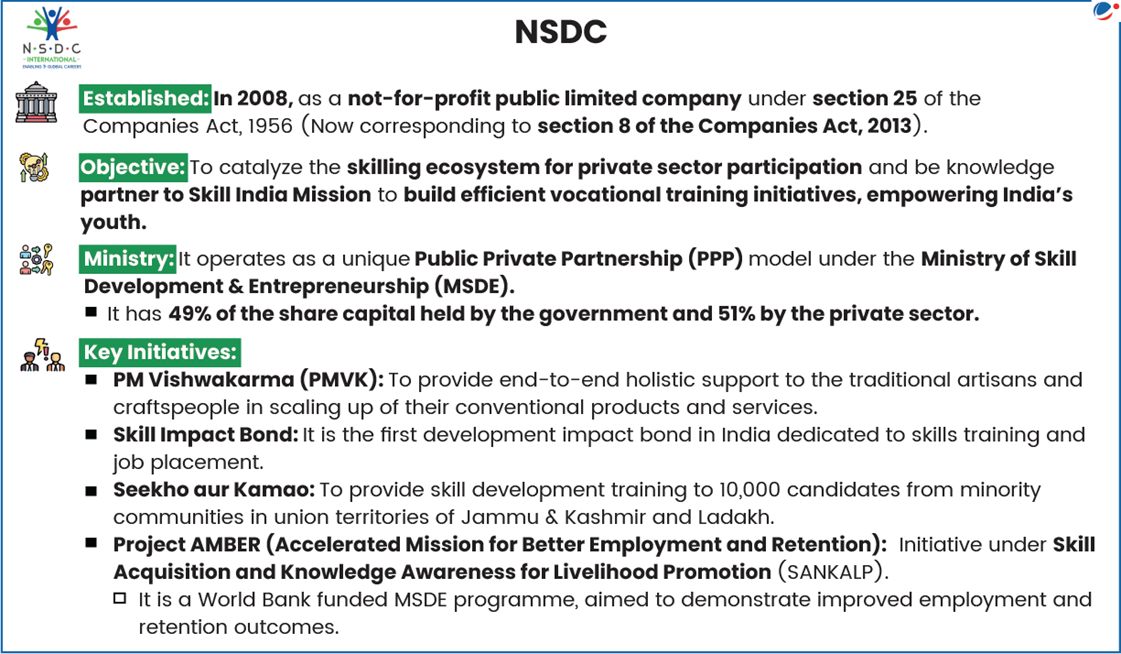
About PMKVY
- Launched: 2015 by Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- Implementing Agency: National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC).
- Aim: To encourage and promote skill development in India.
- Objectives: To enable Indian youth to take up industry-relevant skill training to secure better livelihoods and to recognize informally acquired skills through certification.
- Federal Character: The scheme is managed through Central and State components by earmarking 75 and 25 per cent of physical targets and financial allocations to NSDC and State Skill Development Missions, respectively.
- Achievements: Since 2015, over 1.6 crore youth have been trained nationwide. Across the first three phases, 1.10 crore beneficiaries received skill certification.
Key Issues Highlighted by CAG
- Low Placement Rates: Only 41% of candidates certified under Short Term Training and Special Projects components secured work.
- Placements were heavily concentrated in the Apparel sector (e.g., self-employed tailors).
- Sector Concentration: Five sectors (Apparel, Electronics, Retail, Logistics, and Beauty) accounted for over 58% of all placements.
- Data Integrity Lapses:
- Violation of Eligibility Criteria: Candidates were certified despite ignoring prescribed age, education, and work-experience requirements. For example, 1,142 underage candidates were certified for driver/chauffeur roles.
- Technical Qualification Lapses: In roles requiring prior technical education, 85.40% of certified candidates possessed only basic literacy.
- Inadequate Monitoring:
- Fund underutilisation: Approximately ₹337.16 crore from PMKVY 2.0 remained unutilised as of July 2023. Payouts to over 34 lakh certified candidates have not been made due to insufficient information.
- Skill-Gap Discrepancies: Training is not consistently aligned with the skill requirements identified in the National Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (NPSDE).
- Skill Development Planning Deficit: Phase III envisaged a National Skill Development Plan based on state & district plans. National plan not prepared; only 2 of 8 selected states prepared state plans.
- Fictitious Agencies: Certifications were awarded through agencies that were either non-existent or ineligible.
- Bank Accounts: Bank details for 94.53% of participants (over 90 lakh cases) were entered as zero, 'null', or left blank.
- Invalid Entries: Use of placeholder emails like "abc@gmail.com" and mobile numbers like "1111111111" was widespread.
- Same Photographs: The audit found identical photos used for different certification batches across different states.
- Closed Centres: Physical surveys revealed that several Training Centres (TCs) were closed during the training period.
Recommendations by CAG
- Market Alignment: MSDE should align skill training with micro-level skill gaps and job-role demands across states.
- Strategic Planning: Expedite the preparation of the National Skill Development Plan (NSDP) to provide long-term continuity.
- Integration with UDISE: Use the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE) database to better identify and verify school/college dropouts for onboarding.
- Strict IT Controls: Enforce mandatory Aadhaar-based e-KYC and system validation checks to prevent duplicate or invalid data entries.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Establish a data retention policy and strengthen oversight of post-training assessment activities.
Conclusion
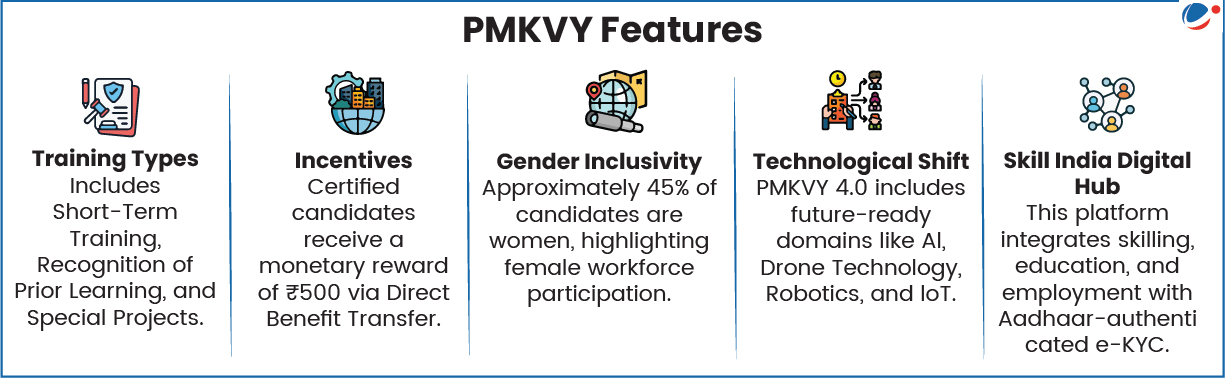
While PMKVY has built a massive infrastructure for short-term skilling in India, the CAG audit reveals significant systemic vulnerabilities in data management and outcome tracking. Transitioning to PMKVY 4.0 offers an opportunity to rectify these issues by leveraging the Skill India Digital Hub (SIDH) for better transparency and ensuring that skilling efforts lead to meaningful employment rather than just certification.