Why in the news?
The 'Smuggling in India report 2024-25' by the Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) highlighted the increasing use of Stablecoins and cryptocurrency for illicit payments of crime particularly in drug and gold smuggling.
About cryptocureencies and Stablecoins
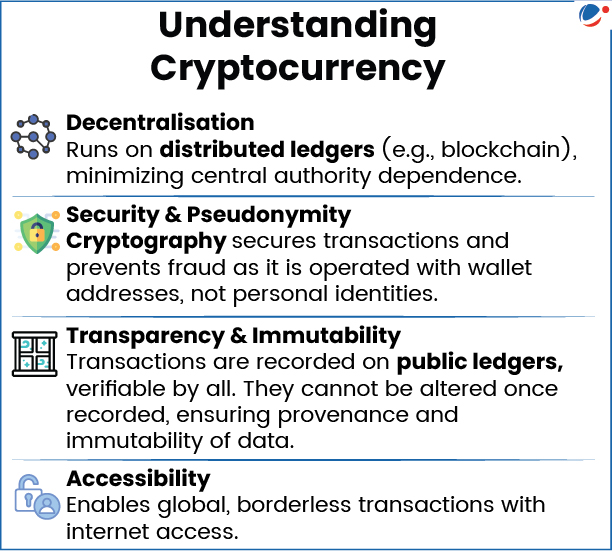
- Cryptocurrency: Form of digital currency (based on the blockchain technology) that utilizes a unique software code. E.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.
- Blockchain is an open-source database (public ledger) distributed across a decentralized computer network/internet that forms a permanent record of transactions between parties.
- They are Non fiat (functions independently of government/Central Bank); have no intrinsic Value, etc.
- Stablecoins: They are a type of cryptocurrency whose value is pegged to another asset, such as a fiat currency or gold, to maintain a stable price.
Reasons for use of Cryptocurrencies/stablecoins in Smuggling
- Decentralized: It allows a difficult-to-trace environment through dark web marketplaces for sale of drugs supplied by organized crime syndicates across borders due to its uthorization, and borderless nature.
- E.g., stable-coins like USDT are increasingly replacing traditional hawala networks.
- Off-the-book payments: Crypto wallets, often anonymous and accessible via VPNs, facilitate off-the-book illicit payments, including for under-invoiced and misdeclared imports allowing smugglers to evade customs duties and taxes.
- Pseudonymous nature: Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin allow fraudsters to conceal their identities, hindering detection and enforcement.
- Regulatory Gaps & Jurisdictional Issues: Law enforcement agencies face significant challenges due to fragmented regulatory landscape, need of advanced blockchain forensics and uthorizati analytical tools to trace illicit flows.
Regulation of Cryptocurrencies
|
Way forward
- Stronger regulatory frameworks: E.g., mandating source-of-funds verification for all Virtual Digital Asset (VDA) transactions above ₹1 lakh, establishing a uthorizati crypto transaction registry linked to PAN/Aadhaar etc.
- Enhanced Anti Money Laundering (AML) compliance: Integrate VDAs fully into existing AML frameworks to trace illicit proceeds from drug/gold smuggling syndicates.
- E.g., PMLA enforcement can be strengthened by requiring mandatory KYC and real-time transaction reporting from all VDA platforms.
- Advanced forensic tools: Develop dedicated blockchain forensics units within DRI and ED, equipped with AI-driven analytics to track uthorization wallet movements, VPN-enabled transactions, and cross-border cryptocurrency flows.
- Global cooperation: Negotiate bilateral Multilateral agreements with crypto hubs for intelligence sharing on international syndicates.
Conclusion
The growing use of cryptocurrencies and stablecoins in smuggling reflects how digital anonymity and regulatory gaps are being exploited by uthoriza crime networks. Strengthening AML frameworks, blockchain forensics, and international cooperation is essential to curb illicit crypto-enabled trade while safeguarding financial integrity.






