Why in the News?
National Project for Strengthening Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) Initiatives in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) has been approved with an outlay of ₹507.37 crores.
About Community-based Disaster Risk Reduction (CBDRR)
- CBDRR is the active engagement of the community in identification, analysis, assessment, monitoring, implementation and evaluation of disaster risks to reduce their vulnerabilities and enhance capacities.
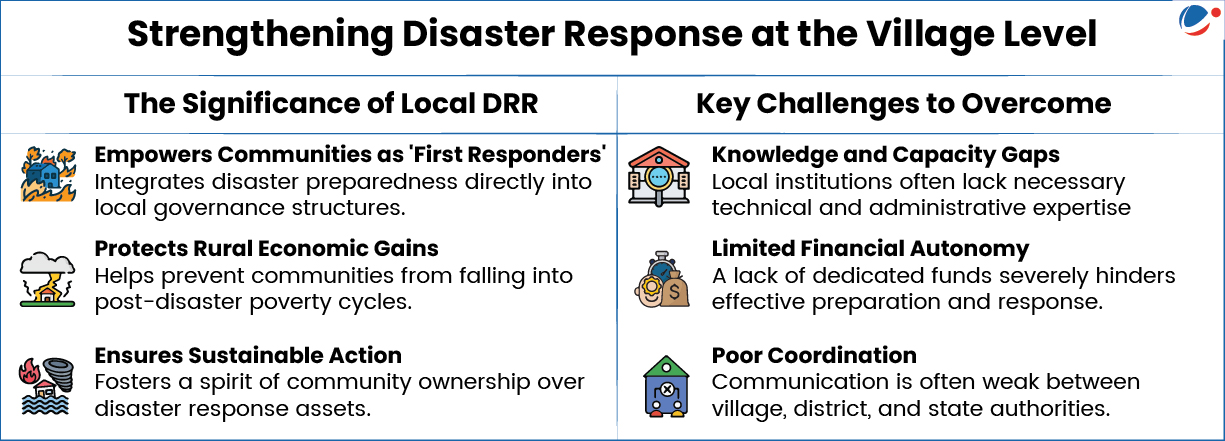
- Benefits: Participatory Risk Assessment and Planning, effective information dissemination, local knowledge and contextual understanding, communities are 1st responders to disasters.
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015-30) calls for CBDRR.
About the National Project for Strengthening Community-Based DRR
- Aim: To integrate DRR into local governance through a bottom-up approach, positioning PRIs as the backbone of disaster preparedness, mitigation and resilience at grassroots level.
- Joint Implementation: By Ministry of Panchayati Raj (MoPR) and National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
- Coverage: 20 States across India, covering 81 disaster-prone districts.
- Cluster-Based Model: 20 Gram Panchayats (GPs) in each district will be covered.
- Model Gram Panchayats: 20 GPs (one per state) will be developed as "Model Gram Panchayats" focusing on 6 specific hazard themes (e.g. floods, earthquakes, etc.).
- They will serve as demonstrative templates for integrating disaster resilience into planning, infrastructure and community preparedness.
Key Initiatives for Local-Level Disaster Management
- Disaster Management Plan (DMP-MoPR): Integration of disaster management into the Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDP).
- Aapda Mitra Scheme: Training community volunteers in disaster response to assist local PRIs.
- Digitization: Leveraging digital platforms to integrate disaster management planning, track expenditures, and disseminate real-time information to Panchayats. For example,
- eGramSwaraj: Simplified Work Based Accounting Application for Panchayati Raj ensuring transparency in the decentralised planning
- Gram Manchitra: Spatial mapping tool for planning and decision-making for Panchayats.
- SACHET: Common Alerting Protocol (CAP) based National Disaster Alert Portal.
- CAP is the international standard format for emergency alerting and public warning adopted by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
Way Forward
- Mainstreaming DRR: Disaster resilience must become a standard part of all infrastructure projects. E.g. roads, schools, clinics.
- Nature-based Solutions: Restoring natural ecosystems (e.g. mangroves, wetlands, forests) provides benefits like water security, biodiversity protection, vital for long-term rural resilience.
- Scaling Up: The learnings from the 20 Model GPs should be scaled to all 2.5 lakh+ Gram Panchayats in India.
- Financial backing: Effective allocation and use of funding from State Disaster Mitigation Funds (SDMF).
- Technological Integration: Providing PRIs with access to user-friendly apps and satellite-based early warning alerts and training for their adoption.
Local Best Practices
|
Conclusion
The boost to the National Project is a step in the right direction to make PRIs and local communities "Disaster Resilient." By empowering the local governments in DRR, disaster management will no longer be just a reactive state function but a proactive "way of life" at the grassroots level.





