Recently, the Russian president visited New Delhi for the 23rd India–Russia Annual Summit, which marked the 25th anniversary of the Declaration on Strategic Partnership (2000).
Key outcomes of the summit
- Trade target: A revised trade target was set at USD 100 billion by 2030, accompanied by the adoption of “Programme 2030” for economic cooperation.
- Programme 2030 focus on diversifying trade beyond energy and defence.
- Cooperation in International Fora: Russia formally joined the India-led International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA), which is an India led collation of Big cat range and non-range countries.
- IBCA (HQ in New Delhi) seeks to conserve 7 big cats - Tiger, Lion, Leopard, Snow Leopard, Cheetah, Jaguar, and Puma.
- Currency & Payments: To bypass Western-led financial restrictions, both agreed to continue developing rupee–ruble settlements, payment system interoperability, etc.
- Currently, nearly 96% of bilateral trade is already settled using national currencies.
- Fossil Fuels and fertilisers: Russia reaffirmed the uninterrupted supply of oil, gas, coal and fertilisers to India, despite external pressures
- India is the second-largest importer of fossil fuels globally.
- Civil Nuclear Energy: Russia committed to uninterrupted oil and gas supplies and continued support for India’s civil nuclear programme (Kudankulam, small modular reactors).
- Labour Mobility: A Migration and Mobility agreement was signed to facilitate the legal entry of skilled Indian workers into Russia to address its labour shortages
- Arctic Cooperation: Russia invited India to deepen engagement in Arctic, including the MOU on training of Indian seafarers for polar waters.
- With 13% of global undiscovered oil and 30% of gas reserves, the Arctic holds significant economic and strategic value.
WSIS+20 marks the 20th anniversary review of the World Summit on the Information Society, Convened under the auspices of the United Nations.
World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS)
- It is a 2 phase UN Conference that defined the issues, policies and frameworks to tackle the Information and Communication technologies to foster development.
- Phase I: Geneva, 2003, Adopted Declaration of Principles and Plan of Action
- Phase II: Tunis, 2005, Adopted Tunis Agenda for the Information Society
- Since then, many WSIS-related events have been held, including the annual WSIS Forums, as well as the review process WSIS+10 and the forthcoming WSIS+20.
- Objective:
- It is a multistakeholder UN process on digital governance and cooperation with a vision of fostering people-centered, inclusive, and development-oriented information and knowledge societies.
- Build a people-centered, inclusive, and development-oriented information society by ensuring universal access to information and ICTs, reducing digital divides, and leveraging digital technologies for sustainable development
- WSIS forum is co-organised annually by ITU, UNESCO, UNDP, and UNCTAD and co-hosted by ITU and the Swiss Confederation.
- Review Process: WSIS+10 and WSIS+20 review mechanisms
Article Sources
1 sourceIndia has been re-elected to the International Maritime Organization (IMO) Council for 2026–27 with highest votes
- IMO Council consists of 40 elected members across three categories (A,B and C) and functions as the executive body of the IMO.

Role of IMO in Maritime Safety
- Key IMO Conventions and Strategies
- International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) prevents and minimizes pollution (oil, garbage, air) from ships.
- Ballast Water Management Convention aims to prevent the spread of invasive aquatic species.
- International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) establishes minimum safety standards for ships, including requirements for fire protection and navigation.
- International Convention on Standards for Training Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers Convention sets qualifications for seafarer training and certification.
- 2023 IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships seeks to achieve net-zero GHG emissions by 2050.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe World Telecommunication Development Conference (WTDC-25) (held every four years) of ITU concluded in Baku.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU) (Hq: Geneva, Switzerland)
- Overview: United Nations Specialized agency for digital technologies (ICTs).
- Members: 194 Member States, and more than 1000 companies, universities, etc.
- Genesis: 1865, after the first International Telegraph Convention was signed in Paris establishing International Telegraph Union (first incarnation of ITU).
- Key Functions:
- Manages Key Resources: Allocates radio frequencies and satellite positions.
- Sets the Rules: Creates technical standards for seamless global connectivity.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe Three Seas Initiative (3SI) marked a decade since its conceptual inception (2015).
About Three Seas Initiative (3SI)
- It is an intergovernmental forum comprising 13 member states situated between the Baltic, Adriatic, and Black Seas.
- Formation: Established in 2015 by the former presidents of Poland and Croatia, it functions as a regional cooperation that complements EU policies.
- Membership: Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Estonia, Greece, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia.
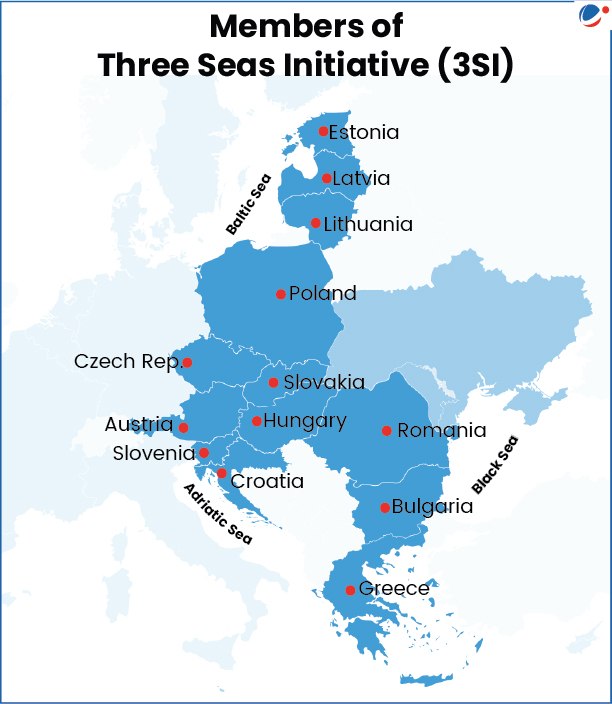
- Aim: The Three Seas initiative aims to promote cooperation for the development of infrastructure in the energy, transport, and digital sectors.
- Three Seas Initiative Investment Fund (3SIIF): Established in 2019, aimed at reducing reliance on national and EU public financing.
- Objectives:
- Economic & Energy Security: Fosters growth in Central & Eastern Europe while reducing dependence on Russian energy.
- Connectivity Rebalancing: Overcomes Soviet-era East–West dominance by promoting North–South transport, energy, and digital corridors.
- Strategic Integration: Strengthens EU cohesion and reinforces the region’s role within EU and NATO frameworks.
- IMEC Linkage: Acts as a northern extension of the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor, linking Mediterranean ports to Central & Eastern Europe and the Baltics.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, the washing accord for peace and prosperity was signed between Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Rwanda, facilitated by the United States.
- Background: Earlier Rwanda-backed M23 rebels launched new attacks in eastern DRC, fuelling displacement and regional tensions.
About the accord
- Aim - To restore trust between these two countries and ensuring lasting peace in mineral rich Eastern DRC regions such as Katanga, Kivu, Ituri, etc.
- DRC is known for its mineral such as copper and cobalt, tin, tungsten, tantalum, gold and diamond.
- It’s the world’s largest cobalt producer, (70 % of global supply chain).
Recently, the UN General Assembly adopted the resolution supporting the United Nations Convention on Negotiable Cargo Documents (Accra Convention), 2025.
- Negotiable Cargo Documents (NCDs) are documents (both in paper and digital format) that represent goods in transit, and confer rights over goods to the holder which are transferrable.
About Accra Convention, 2025
- Objective: Establishes a uniform legal framework for NCDs and extends benefits of negotiable documents beyond maritime transport to multimodal transport (train, truck, plane, or ship).
- It allows cargo to be sold, rerouted, or used as collateral for financing while it is mid-journey.
- Legal Effect: NCDs have the same legal effect as physical delivery of goods.
- Significance: facilitates trade finance, digitalisation of global trade, etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceIsrael became the first country to formally recognise the self-declared Republic of Somaliland as an independent and sovereign state.
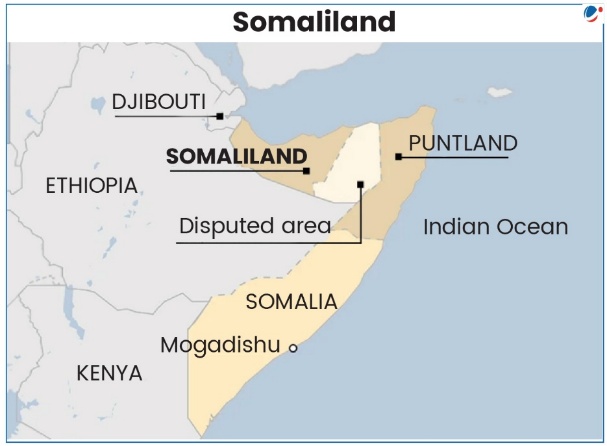
About Republic of Somaliland
- Location: It is located in the Horn of Africa and borders the Gulf of Aden (North), Djibouti (Northwest), Ethiopia (South and west), and Somalia (East).
- It broke away from Somalia in 1991 after the collapse of the central government and years of civil war. Since then, it has functioned as a de facto state, with its own elected government.
- Capital: Hargeisa
Kuwait signed an agreement with China to build Mubarak Al-Kabeer Port.
About Mubarak Al-Kabeer Port
- Location: Boubyan Island, Kuwait.
- Aim: Enhance regional trade and transportation, contributing to Kuwait’s economic diversification, reducing its reliance on oil.
- Part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI): BRI or New Silk Road, is China-led infrastructure projects launched in 2013. It has two components:
- Silk Road Economic Belt: Land routes across Europe, Middle East, Central Asia and Asia.
- Maritime Silk Road: Sea routes across East Asia, South Asia, Middle East and Africa.
The Kimberley Process (KP) Plenary has selected India to assume the chairpersonship of the KP from 1 January 2026.
About Kimberley Process
- It is a tripartite initiative involving governments, the international diamond industry and civil society, aimed at preventing the trade in “conflict diamonds”.
- Conflict Diamonds are rough diamonds used by rebel movements or their allies to finance armed conflicts aimed at undermining legitimate governments.
- Members: 60 participants including India and European Union, accounting for over 99% of global rough diamond trade.
- By enforcing rigorous certification protocols and compliance assessments, it ensures that all participating countries maintain high standards that keep conflict diamonds out of the international market.






